
Medical terminology suffixes and their meanings made easy! List of common suffixes along with examples, flashcard tables, and a review of prefixes and root words!
Save time by watching the video first, then supplement it with the lecture below!
Click below to view the EZmed video library. Subscribe to stay in the loop!
Instant access to a members-only page of ALL the flashcards, study guides, and PDF lectures. Cancel anytime.
Click below to download your flashcards & study guides to SAVE TIME studying, PASS your classes, and SUCCEED in medicine!



Set aside the medical terminology course books, flashcards, and dictionaries for a moment!
You have landed on a page where medical terminology is simplified for you!
Filled with common prefixes, root words, and suffixes you are likely to encounter, our medical terminology series will provide you with condensed high-yield information.
We already reviewed common medical abbreviations, prefixes, and root words in previous posts - see below!
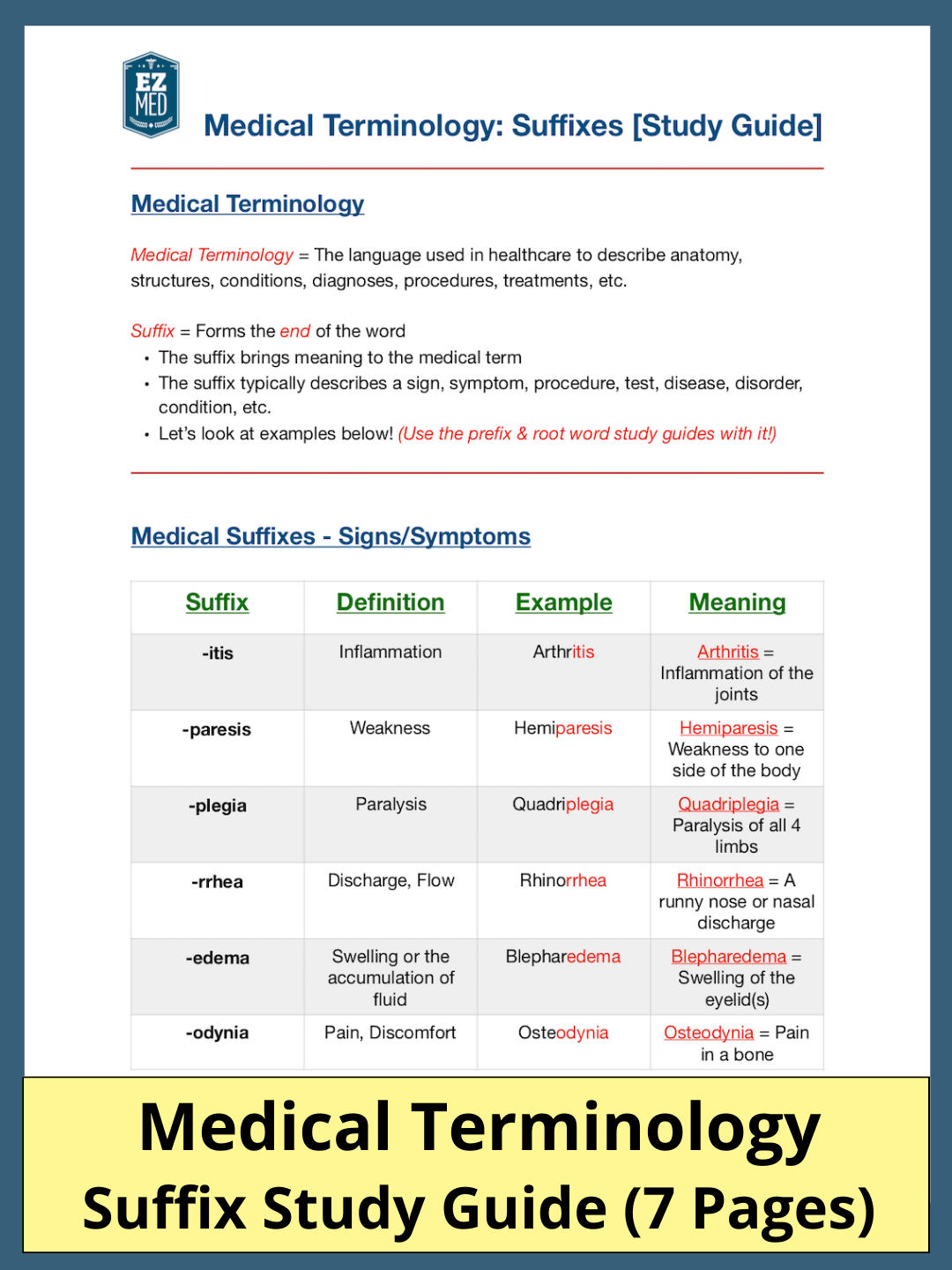
Now let’s focus on common suffixes and their meanings!
We will review suffixes pertaining to procedures, tests, signs, symptoms, diseases, diagnoses, conditions, and much more!
You will learn the meanings for common medical suffixes including -osis, -oma, -itis, -ism, -plasty, -al, -tomy, -gram, -ic, -ologist, -spasm, and many more!
You will also be provided with tables to quiz yourself, as well as examples to help you remember them all!
Let’s get started!
Enjoy all of our simplified medical terminology posts!
Medical Suffixes MADE EASY! - Currently Viewing
Medical terminology is the language used in healthcare to describe anatomy, structures, conditions, diagnoses, procedures, treatments, and much more.
Let’s briefly recap the word elements that make up medical terms.
If you are coming to this post from one of our other medical terminology lectures, then this section will be a great review!
Most medical words have a beginning, middle, and end.
They are referred to as the prefix, root, and suffix.
The prefix is at the beginning.
The root is in the middle.
The suffix is at the end.
The simplest approach to take when figuring out the meaning of a medical term is to break down the word into its different parts.
The prefix is typically the descriptive part of the medical term, and it forms the beginning of the word.
The prefix describes characteristics such as a location, direction, number, quantity, amount, size, or color.
The root provides the subject of the medical term.
It is the core meaning of the word, and it often pertains to a body part or system.
The root forms the middle of the word when a prefix is present.
If there is no prefix, then the root will form the beginning of the word.
Some medical terms may also have more than one root word combined together.
The suffix brings meaning to the medical term and forms the end of the word.
The suffix might indicate a disease, disorder, condition, procedure, process, specialty, test, or status.
As mentioned above, medical suffixes bring meaning to the term and often describe a procedure, test, diagnosis, condition, or process.
Let’s review common medical suffixes, along with their meanings and examples, starting with terms related to procedures.
Of note, many of the suffixes listed below start with the letter “O”.
This is called the combining vowel.
The combining vowel is the vowel that follows the root word and connects the root to another root or a suffix.
Be aware that a different vowel other than “O” may be used to connect the word elements together.
-ostomy = To surgically create an artificial opening or stoma
Therefore, colostomy is a surgery that creates a new opening for the colon to pass through the abdominal wall.
-otomy = To make an incision or cut into
Therefore, laparotomy is a surgical incision into the abdominal cavity.
Be careful with “-ostomy” and “-otomy” as they sound similar.
-ectomy = The surgical removal or excision of
Therefore, nephrectomy is the surgical removal of a kidney or part of a kidney.
-oscopy = The examination or viewing of (especially with a scope - an instrument used to view or observe)
Examples: Cystoscopy, Colonoscopy, or Arthroscopy
You can figure out the body part being viewed by breaking down the root word, most of which we learned in the previous root word lectures.
“Cysto-” refers to bladder, so cystoscopy is the use of a scope to visualize the inside of the bladder.
“Colo-” refers to colon, so colonoscopy is the use of a scope to visualize the inside of the colon.
“Arthro-” refers to joint, so arthroscopy is the use of a scope to visualize the inside of a joint.
-centesis = To puncture or the aspiration of
Examples: Pericardiocentesis, Thoracentesis, or Arthrocentesis.
Again the root word will help you determine what part of the body is being punctured or aspirated.
“Pericardio-” refers to the pericardium (sac around the heart), so pericardiocentesis is a procedure that uses a needle to aspirate or remove fluid from the pericardial sac.
“Thora-” refers to the chest or thorax, so thoracentesis is the aspiration of fluid or air from the pleural space of the chest cavity (space between the lungs and chest wall).
“Arthro-” refers to joint, so arthrocentesis is the puncture of a joint especially for the aspiration of fluid from the joint space.
-plasty = A surgical procedure for the repair, restoration, or replacement of a part of the body
Therefore, rhinoplasty is a surgery that changes the shape of the nose.
-otripsy = Crushing
Therefore, lithotripsy refers to a procedure that crushes a stone (such as a kidney stone).
-desis = Binding or fusing together
Pleurodesis is the procedure of fusing or adhering the layers of the pleura together.
Remember the pleura is the thin membrane covering the lungs and also lines the inside of the chest wall.
Therefore, a pleurodesis prevents the build up of fluid or air in the pleural cavity.
-scope = The instrument used to view or observe a body part
We alluded to this above when discussing the suffix “-oscopy” which pertained to procedures that used a scope to view or examine a part of the body.
Again the root word will describe what part of the body the instrument is used for.
Examples: Otoscope or Ophthalmoscope
Therefore, an otoscope is the instrument used to examine the ear, and an ophthalmoscope is the instrument used to view and examine the eye.
-opsy = Examination or Inspection of
Example: Biopsy or Autopsy
A biopsy is the removal of cells or tissues for examination (typically by a pathologist).
An autopsy is the examination of a body after death to determine a cause or to examine the extent of a disease.
Now it’s your turn!
Cover up the second column of the table below and see how many suffixes you can define!